Diagnosis of heart failure in dogs. Clinical analysis.
 Determination of the physical condition of the dog
Determination of the physical condition of the dog
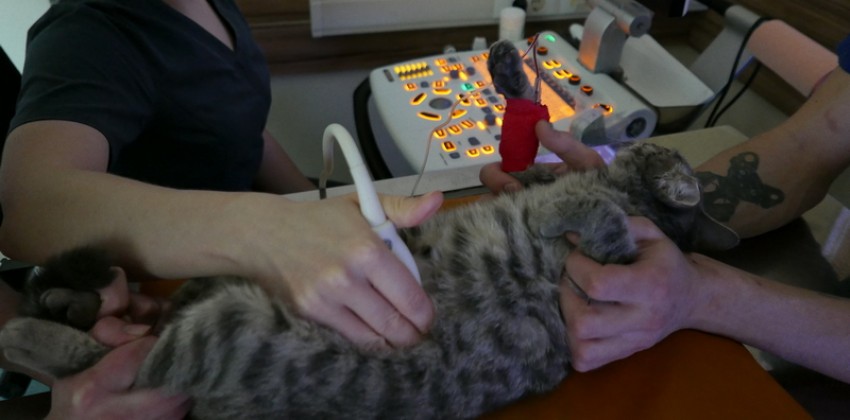
During a medical examination of a patient with signs of circulatory insufficiency, it is necessary to take into account body temperature, weight and condition of muscles, skin and hair, as well as the presence of swelling of the limbs. It is necessary to carry out palpation of the abdominal cavity in order to identify the state of the liver, the presence of ascites and tumors. Then you need to examine the chest (whether there is apical impulse or trembling) and check the heart rate, the nature of the pulse and heart pushes. After that, an examination of the sclera, gums and oral mucosa is carried out to detect cyanosis. Examination should be carried out when the dog is at rest, and then, for comparison, after exercise. After this, the readings are compared. Care must be taken in determining the load for dogs with pronounced circulatory insufficiency and for those that during the examination in the veterinary clinic detect an inadequate reaction.
Auscultation.
Best of all, the heart is tapped with a stethoscope. Auscultation should be carried out according to the appropriate methodology to identify any permanent indicators and compare them with data from other surveys. It should cover at least four areas associated with heart valves (Fig. 11), and be carried out in the same sequence each time. At first, all four areas are heard in a standing position, then in a sitting position and, finally, lying on the right and on the left side. Auscultation is a very reliable and effective method for detecting clinical cases of heart disease. This is the easiest way to determine heart rate and heart rate. Abnormal heart sounds manifest as cardiac arrhythmias or noise. In the first case, we are talking about changes in the frequency or rhythms of heart tones, in the second – about changes in their nature or quality due to pathological disorders in the cardiovascular system.
Arrhythmia.
The most common form of arrhythmia in dogs, with the exception of cases of normal sinus arrhythmia, is the appearance of premature ventricular systole. She has always been associated with heart disease in dogs. A characteristic feature of this type of arrhythmia is a disturbance of the normal heartbeat and the appearance of one or two premature contractions. An abnormally long compensatory pause may occur between premature and subsequent normal contraction of the heart.
Atrial fibrillation.
Perhaps this is the most serious type of arrhythmia in dogs, which in almost all cases leads to the most serious consequences. Atrial fibrillation is often associated with an increase in atrial size, especially in chronic valvular heart disease. It is characterized by irregular heartbeat. If untreated, the heart rate can reach 180 – 220 or more beats per minute. After treatment with digitalis, the heart rate may more or less normalize. But even in this case, the heart rhythm remains uneven.
Galloping rhythm.
Although the disease is not an arrhythmia in the strict sense, it falls under this classification. With a disease, heart sounds resemble the hooves of a galloping horse: each heart beat is accompanied by three audible sounds. True, the extra sounds can be heard at any phase of the cardiac cycle, but the most common and important from the point of view of diagnosis is the protodiastolic gallop or the appearance of an audible third tone. Most often this is due to circulatory failure, and the predictions in this case are very disappointing.
Heart murmurs.
Systolic noise.
Systolic murmurs are observed during systole between the first (Si) and second (S2) cardiac tones. Systolic noise – the most common type of noise in dogs, found during auscultation. It should be borne in mind that their appearance does not always indicate pathological changes in the heart of the animal. Systolic noise, not accompanied by pathological changes, are considered functional noise. The most common pathological disorders associated with systolic murmurs are mitral valve insufficiency and aortic stenosis. Systolic murmurs can also appear in the case of congenital heart defects, when atrial and ventricular septums are affected.
Mitral noises.
Mitral noises are pansystolic noises of constant saturation appearing between the first and second heart tones. Their strength can reach a level at which they completely drown out heartbeats. This is a classic example of noise arising in the case of ventricular and atrial insufficiency, which are of mitral origin. These noises are heard in the area of the mitral valve with mitral insufficiency.
When stenosis of the mouth of the aorta arise midystole noise. In the middle of systole, increased intensity noise is observed.